Butofilolol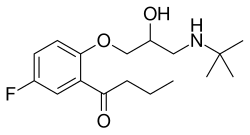 |
|
| Other names | CM-6805 |
|---|
| ATC code | |
|---|
|
(RS)-1-[2-[3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-5-fluorophenyl]butan-1-one
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.892 |
|---|
|
| Formula | C17H26FNO3 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 311.397 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
Fc1ccc(OCC(O)CNC(C)(C)C)c(c1)C(=O)CCC
|
InChI=1S/C17H26FNO3/c1-5-6-15(21)14-9-12(18)7-8-16(14)22-11-13(20)10-19-17(2,3)4/h7-9,13,19-20H,5-6,10-11H2,1-4H3  Y YKey:NMBNQRJDEPOXCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N  Y Y
|
Butofilolol (trade name Cafide) is a beta-blocker drug for the treatment of essential hypertension (high blood pressure).[1][2] It is not known to be marketed anywhere.
It is an example of a butyrophenone.
Synthesis
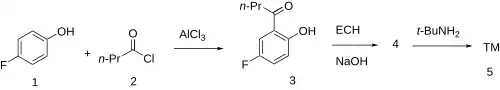
The Fries rearrangement of the ester formed by 4-fluorophenol (1)[3] and butryryl chloride (2) gives 5'-fluoro-2'-hydroxybutyrophenone (3). Treatment with epichlorohydrin in the presence of base leads to 1-[5-fluoro-2-(oxiranylmethoxy)phenyl]butan-1-one (4). Lastly, reaction with tert-butylamine gives butofilolol.[4][5]
References
- ^ Houin G, Barre J, Jeanniot JP, Ledudal P, Cautreels W, Tillement JP (1984). "Pharmacokinetics of butofilolol (CAFIDE) after repeated oral administration in man". International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Research. 4 (3): 175–83. PMID 6149195.
- ^ Toussain P, Gay G, Debry G (June 1983). "[Long-term hypotensive treatment by butofilolol]". Annales de Cardiologie et d'Angeiologie. 32 (4): 277–83. PMID 6412614.
- ^ Mercier C, Youmans P (1996). "4-fluorophenol: A key intermediate for agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals". The Roots of Organic Development. Industrial Chemistry Library. Vol. 8. pp. 293–300. doi:10.1016/S0926-9614(96)80020-7. ISBN 978-0-444-82434-9.
- ^ Castañer J, Neuman M (1982). "Butofilolol". Drugs of the Future. 7 (2): 96. doi:10.1358/dof.1982.007.02.199366.
- ^ US 4252825, Demarne H, "ompositions for treatment of cardiovascular conditions associated with overproduction of catecholamines", issued 24 February 1981, assigned to C. M. Industries )
|
|---|
| α1 | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- Abanoquil
- Ajmalicine
- Alfuzosin
- Anisodamine
- Anisodine
- Atiprosin
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., brexpiprazole, clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone)
- Benoxathian
- Beta blockers (e.g., adimolol, amosulalol, arotinolol, carvedilol, eugenodilol, labetalol)
- Buflomedil
- Bunazosin
- Corynanthine
- Dapiprazole
- Domesticine
- Doxazosin
- Ergolines (e.g., acetergamine, ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, lisuride, nicergoline, terguride)
- Etoperidone
- Fenspiride
- Hydroxyzine
- Indoramin
- Ketanserin
- L-765,314
- mCPP
- Mepiprazole
- Metazosin
- Monatepil
- Moxisylyte
- Naftopidil
- Nantenine
- Neldazosin
- Niaprazine
- Niguldipine
- Pardoprunox
- Pelanserin
- Perlapine
- Phendioxan
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Phentolamine
- Phenylpiperazine antidepressants (e.g., hydroxynefazodone, nefazodone, trazodone, triazoledione)
- Piperoxan
- Prazosin
- Quinazosin
- Quinidine
- Silodosin
- Spegatrine
- Spiperone
- Talipexole
- Tamsulosin
- Terazosin
- Tiodazosin
- Tolazoline
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, maprotiline, mianserin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, clomipramine, doxepin, imipramine, trimipramine)
- Trimazosin
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Urapidil
- WB-4101
- Zolertine
|
|---|
|
|---|
| α2 | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- 1-PP
- Adimolol
- Amesergide
- Aptazapine
- Atipamezole
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine, brexpiprazole, clozapine, lurasidone, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, zotepine)
- Azapirones (e.g., buspirone, gepirone, ipsapirone, tandospirone)
- BRL-44408
- Buflomedil
- Cirazoline
- Efaroxan
- Esmirtazapine
- Fenmetozole
- Fluparoxan
- Idazoxan
- Ketanserin
- Lisuride
- mCPP
- Mianserin
- Mirtazapine
- NAN-190
- Pardoprunox
- Phentolamine
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Piperoxan
- Piribedil
- Rauwolscine
- Rotigotine
- Setiptiline
- Spegatrine
- Spiroxatrine
- Sunepitron
- Terguride
- Tolazoline
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Yohimbine
|
|---|
|
|---|
| β | |
|---|
- See also: Receptor/signaling modulators
- Dopaminergics
- Serotonergics
- Monoamine reuptake inhibitors
- Monoamine releasing agents
- Monoamine metabolism modulators
- Monoamine neurotoxins
|

