Linsitinib
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
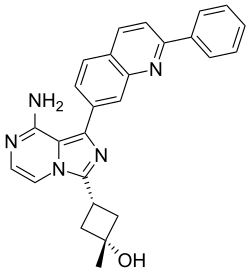
(1s ,3s )-3-[8-Amino-1-(2-phenylquinolin-7-yl)imidazo[1,5-a ]pyrazin-3-yl]-1-methylcyclobutan-1-ol
Other names
OSI-906
Identifiers
CAS Number
3D model (JSmol)
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
DrugBank
KEGG
UNII
InChI=1S/C26H23N5O/c1-26(32)14-19(15-26)25-30-22(23-24(27)28-11-12-31(23)25)18-8-7-17-9-10-20(29-21(17)13-18)16-5-3-2-4-6-16/h2-13,19,32H,14-15H2,1H3,(H2,27,28)
Key: PKCDDUHJAFVJJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/C26H23N5O/c1-26(32)14-19(15-26)25-30-22(23-24(27)28-11-12-31(23)25)18-8-7-17-9-10-20(29-21(17)13-18)16-5-3-2-4-6-16/h2-13,19,32H,14-15H2,1H3,(H2,27,28)/t19-,26+
Key: PKCDDUHJAFVJJB-VLZXCDOPBI
C[C@]1(C[C@@H](C1)C2=NC(=C3N2C=CN=C3N)C4=CC5=C(C=CC(=N5)C6=CC=CC=C6)C=C4)O
Properties
Chemical formula
C 26 H 23 N 5 O
Molar mass
421.504 g·mol−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Linsitinib is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of various types of cancer. It is an inhibitor of the insulin receptor and of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R).[ 1] [ 2]
Linsitinib was granted orphan drug designation for adrenocortical carcinoma in March 2012.[ 3]
Phase II clinical trials were initiated for multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and NSCLC, but subsatisfactory results caused research for these indications to be discontinued.[ 3] [ 4] [ 3]
References
^ Mulvihill, Mark J; Cooke, Andrew; Rosenfeld-Franklin, Maryland; Buck, Elizabeth; Foreman, Ken; Landfair, Darla; O’Connor, Matthew; Pirritt, Caroline; Sun, Yingchaun; Yao, Yan; Arnold, Lee D; Gibson, Neil W; Ji, Qun-Sheng (September 2009). "Discovery of OSI-906: a selective and orally efficacious dual inhibitor of the IGF-1 receptor and insulin receptor". Future Medicinal Chemistry . 1 (6): 1153– 1171. doi:10.4155/fmc.09.89 . PMID 21425998 . ^ "Linsitinib" . NCI Drug Dictionary . National Cancer Institute . Retrieved October 16, 2012 .^ a b c "Linsitinib - AdisInsight" . adisinsight.springer.com .^ Fassnacht, Martin; Berruti, Alfredo; Baudin, Eric; Demeure, Michael J; Gilbert, Jill; Haak, Harm; Kroiss, Matthias; Quinn, David I; Hesseltine, Elizabeth; Ronchi, Cristina L; Terzolo, Massimo; Toni Choueiri; Poondru, Srinivasu; Fleege, Tanya; Rorig, Ramona; Chen, Jihong; Stephens, Andrew W; Worden, Francis; Hammer, Gary D (April 2015). "Linsitinib (OSI-906) versus placebo for patients with locally advanced or metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 study". The Lancet Oncology . 16 (4): 426– 435. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70081-1 . hdl:2318/1534804 25795408 .
External links
Angiopoietin
Agonists: Angiopoietin 1Angiopoietin 4 Antagonists: Angiopoietin 2Angiopoietin 3 Kinase inhibitors: AltiratinibCE-245677
Rebastinib CNTF EGF (ErbB)
EGF(ErbB1/HER1)
Agonists : AmphiregulinBetacellulin
EGF (urogastrone)
Epigen
Epiregulin
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF)
Murodermin Nepidermin Transforming growth factor alpha (TGFα) ErbB2/HER2 ErbB3/HER3
Agonists: Neuregulins (heregulins) (1, 2, 6 (neuroglycan C)) ErbB4/HER4
Agonists: BetacellulinEpigen
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF)
Neuregulins (heregulins) (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (tomoregulin, TMEFF))
FGF
FGFR1
Agonists: ErsoferminFGF (1, 2 (bFGF), 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10 (KGF2), 20)
Repifermin
Selpercatinib Trafermin Velafermin FGFR2
Agonists: ErsoferminFGF (1, 2 (bFGF), 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 (KGF ), 8, 9, 10 (KGF2), 17, 18, 22)
Palifermin Repifermin
Selpercatinib Sprifermin
Trafermin Antibodies: AprutumabAprutumab ixadotin FGFR3 FGFR4
Agonists: ErsoferminFGF (1, 2 (bFGF), 4, 6, 8, 9, 19 )
Trafermin Unsorted
HGF (c-Met) IGF
IGF-1
Kinase inhibitors: BMS-754807NVP-ADW742
NVP-AEW541
OSl-906 IGF-2
Agonists : Insulin-like growth factor-2 (somatomedin A)Antibodies: Dusigitumab Xentuzumab (against IGF-1 and IGF-2) Others
Binding proteins: IGFBP (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)Cleavage products/derivatives with unknown target: Glypromate (GPE, (1-3)IGF-1)Trofinetide
LNGF (p75NTR )
Aptamers: Against NGF: RBM-004Decoy receptors: LEVI-04 (p75NTR -Fc) PDGF
Agonists: Becaplermin Platelet-derived growth factor (A, B, C, D) RET (GFL)
GFRα1
Agonists: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)Liatermin GFRα2
Agonists: Neurturin (NRTN) GFRα3 GFRα4
Agonists: Persephin (PSPN) Unsorted
Kinase inhibitors: Agerafenib
SCF (c-Kit) TGFβ Trk
TrkA
Negative allosteric modulators: VM-902AAptamers: Against NGF: RBM-004Decoy receptors: ReN-1820 (TrkAd5) TrkB
Agonists: 3,7-DHF3,7,8,2'-THF
4'-DMA-7,8-DHF 7,3'-DHF
7,8-DHF 7,8,2'-THF
7,8,3'-THF Amitriptyline BDNF BNN-20 Deoxygedunin Deprenyl Diosmetin
DMAQ-B1
HIOC
LM22A-4 N-Acetylserotonin NT-3
NT-4
Norwogonin (5,7,8-THF) R7 R13 TDP6 TrkC
VEGF
Agonists: Placental growth factor (PGF)Ripretinib Telbermin
VEGF (A, B, C, D (FIGF)) Others
Additional growth factors: Adrenomedullin Colony-stimulating factors (see here instead)
Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF)
Ephrins (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, B1, B2, B3)
Erythropoietin (see here instead)Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI; PGI, PHI, AMF)
Glia maturation factor (GMF)
Hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF)
Interleukins /T-cell growth factors (see here instead)Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP; HLP, HGFLP)
Midkine (NEGF2)
Migration-stimulating factor (MSF; PRG4)
Oncomodulin
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP)
Pleiotrophin
Renalase
Thrombopoietin (see here instead)
Wnt signaling proteins Additional growth factor receptor modulators: Cerebrolysin (neurotrophin mixture)
 Media related to Linsitinib at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Linsitinib at Wikimedia Commons