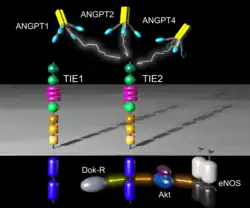
ANGPT1, ANGPT2, and ANGPT4 activate TIE-2. Intracellular signal transduction can proceed via DOK-R (yellow arrow) or alternatively via Akt to eNOS (orange arrow). The angiopoietin receptors are receptors that bind angiopoietin. TIE-1 and TIE-2 comprise the cell-surface receptors that bind and are activated by the angiopoietins, (Ang1, Ang2, Ang3, Ang4). The angiopoietins are protein growth factors required for the formation of blood vessels (angiogenesis ).
Angiopoietins
The angiopoietins are protein growth factors that regulate angiogenesis , the formation of blood vessels. In humans, three angiopoietins have been identified: Ang1, Ang2, and Ang4 (Ang 3 is the mouse ortholog of human Ang4).[ 1] cell signalling .
It is somewhat controversial which of the Tie receptors mediate functional signals downstream of Ang stimulation. But it is clear that at least Tie-2 is capable of physiologic activation as a result of binding the angiopoietins.
See also
Angiopoietin § Tie pathway
References
External links
Protein kinases: tyrosine kinases (EC 2.7.10)
Receptor tyrosine kinases (EC 2.7.10.1)
Growth factor receptors
EGF receptor family Insulin receptor family PDGF receptor family
CSF1R FLT3
KIT
PDGFR (PDGFRA
PDGFRB) FGF receptor family VEGF receptors family HGF receptor family Trk receptor family
EPH receptor family
EPHA1
EPHA2
EPHA3
EPHA4
EPHA5
EPHA6
EPHA7
EPHA8
EPHB1
EPHB2
EPHB3
EPHB4
EPHB5
EPHB6
EPHX LTK receptor family family ROR receptor family DDR receptor family PTK7 receptor family RYK receptor family MuSK receptor family ROS receptor family AATYK receptor family AXL receptor family RET receptor family uncategorised
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases (EC 2.7.10.2)
ABL familyACK family CSK family FAK family FES family FRK family JAK family SRC-A family SRC-B family TEC family SYK family
Enzymes
Activity
Active site
Binding site
Catalytic triad
Oxyanion hole
Enzyme promiscuity
Diffusion-limited enzyme
Cofactor
Enzyme catalysis Regulation Classification
EC number
Enzyme superfamily
Enzyme family
List of enzymes Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics
Eadie–Hofstee diagram
Hanes–Woolf plot
Lineweaver–Burk plot
Michaelis–Menten kinetics Types
EC1 Oxidoreductases (list)EC2 Transferases (list)EC3 Hydrolases (list)EC4 Lyases (list)EC5 Isomerases (list)EC6 Ligases (list)EC7 Translocases (list)
Agonists: Angiopoietin 1Angiopoietin 4 Antagonists: Angiopoietin 2Angiopoietin 3 Kinase inhibitors: AltiratinibCE-245677
Rebastinib CNTF EGF (ErbB)
EGF(ErbB1/HER1)
Agonists : AmphiregulinBetacellulin
EGF (urogastrone)
Epigen
Epiregulin
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF)
Murodermin Nepidermin Transforming growth factor alpha (TGFα) ErbB2/HER2 ErbB3/HER3
Agonists: Neuregulins (heregulins) (1, 2, 6 (neuroglycan C)) ErbB4/HER4
Agonists: BetacellulinEpigen
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF)
Neuregulins (heregulins) (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (tomoregulin, TMEFF))
FGF
FGFR1
Agonists: ErsoferminFGF (1, 2 (bFGF), 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10 (KGF2), 20)
Repifermin
Selpercatinib Trafermin Velafermin FGFR2
Agonists: ErsoferminFGF (1, 2 (bFGF), 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 (KGF ), 8, 9, 10 (KGF2), 17, 18, 22)
Palifermin Repifermin
Selpercatinib Sprifermin
Trafermin Antibodies: AprutumabAprutumab ixadotin FGFR3 FGFR4
Agonists: ErsoferminFGF (1, 2 (bFGF), 4, 6, 8, 9, 19 )
Trafermin Unsorted
HGF (c-Met) IGF
IGF-1
Kinase inhibitors: BMS-754807Linsitinib NVP-ADW742
NVP-AEW541
OSl-906 IGF-2
Agonists : Insulin-like growth factor-2 (somatomedin A)Antibodies: Dusigitumab Xentuzumab (against IGF-1 and IGF-2) Others
Binding proteins: IGFBP (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)Cleavage products/derivatives with unknown target: Glypromate (GPE, (1-3)IGF-1)Trofinetide
LNGF (p75NTR )
Aptamers: Against NGF: RBM-004Decoy receptors: LEVI-04 (p75NTR -Fc) PDGF
Agonists: Becaplermin Platelet-derived growth factor (A, B, C, D) RET (GFL)
GFRα1
Agonists: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)Liatermin GFRα2
Agonists: Neurturin (NRTN) GFRα3 GFRα4
Agonists: Persephin (PSPN) Unsorted
Kinase inhibitors: Agerafenib
SCF (c-Kit) TGFβ Trk
TrkA
Negative allosteric modulators: VM-902AAptamers: Against NGF: RBM-004Decoy receptors: ReN-1820 (TrkAd5) TrkB
Agonists: 3,7-DHF3,7,8,2'-THF
4'-DMA-7,8-DHF 7,3'-DHF
7,8-DHF 7,8,2'-THF
7,8,3'-THF Amitriptyline BDNF BNN-20 Deoxygedunin Deprenyl Diosmetin
DMAQ-B1
HIOC
LM22A-4 N-Acetylserotonin NT-3
NT-4
Norwogonin (5,7,8-THF) R7 R13 TDP6 TrkC
VEGF
Agonists: Placental growth factor (PGF)Ripretinib Telbermin
VEGF (A, B, C, D (FIGF)) Others
Additional growth factors: Adrenomedullin Colony-stimulating factors (see here instead)
Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF)
Ephrins (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, B1, B2, B3)
Erythropoietin (see here instead)Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI; PGI, PHI, AMF)
Glia maturation factor (GMF)
Hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF)
Interleukins /T-cell growth factors (see here instead)Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP; HLP, HGFLP)
Midkine (NEGF2)
Migration-stimulating factor (MSF; PRG4)
Oncomodulin
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP)
Pleiotrophin
Renalase
Thrombopoietin (see here instead)
Wnt signaling proteins Additional growth factor receptor modulators: Cerebrolysin (neurotrophin mixture)