The July 14, 2017 NASA Spaceflight article Soyuz 2-1A launches with Kanopus-V-IK and over 70 satellites says:
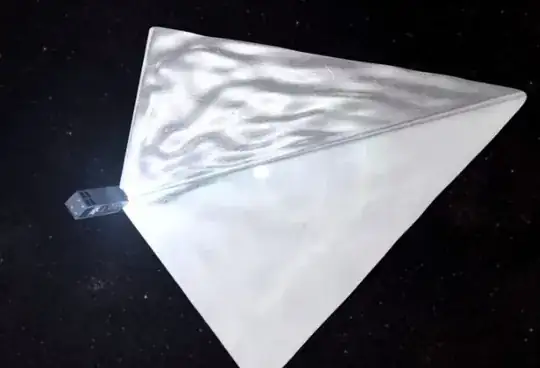
Mayak is a three-unit CubeSat which was built by Tvoii Sektor Kosmosa – or “Your Sector of Space” – an independent, crowd-funded team of engineers in conjunction with the Moscow State University of Mechanical Engineering. Mayak – meaning Lighthouse – will deploy a highly reflective tetrahedral structure.
Each side of this structure has an area of four square meters, or 43 square feet. To ground observers, the satellite is expected to have an apparent magnitude of up to -10, making it one of the brightest objects in the night sky. The structure will double as a deorbit mechanism, hastening the decay of the satellite’s orbit.
While the satellite itself is a 3U cubesat with nominal dimensions of 10x10x30 centimeters, once the reflector is deployed the relatively flat reflecting surfaces are sizeable - each face is 4 square meters.
The reflector material seems to be a metallized polymer film, so it may have some significant UHF reflectivity. The metal could be extremely thin meaning less than 1 micron (1E-06 meters) and so the skin depth may be an issue. So far I have not found many helpful sources of technical information on the project in English - the cubesat project has been carried out in Russia. This web site can switch between English and Russian but so far I can't get to many details there.
There are several issues that might make this difficult. If the satellite does not have any extraordinary orientation control, it may end up random, and possibly rotating at some unknown speed. The sides will certainly not be perfectly flat. The rotation and uneven surface could be beneficial as it is more likely to occasionally reflect at least some radiation from a given pair of transmit and receive sites.
The orbit would not be as stable or regular as other amateur satellites, and in LEO (low Earth orbit) it will be moving fairly fast.
So I'm wondering if an Earth-Satellite-Earth bounce of an amateur signal of any kind might be possible and worth an attempt, and how problematic the issues I've mentioned or probably several I haven't thought of yet might be.
above: Mayak Reflector – Photo: CosmoMayak, From Spaceflight 101
above: Mayak Artists conception, From NASA Spaceflight
As a historic reference, I am reminded a bit of the first ever Earth-Satellite-Earth bounce research with Project Echo in the 1960's.
above: Echo-1 Satellite, test inflation before launch; NSSDCA/COSPAR ID: 1960-009A, satnum 00049, for scale, those are people at the bottom. From NASA