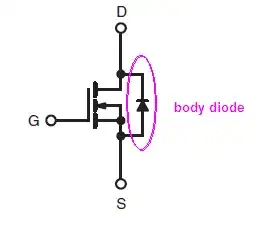
To understand the rationale of AC/DC and DC-only configurations, MOSFET body diode should be considered. In power MOSFETs bulk is connected to source, and that creates a diode in parallel with the MOSFET channel.
The picture below is from the datasheet of IRF510. It's a generic power N-channel MOSFET.
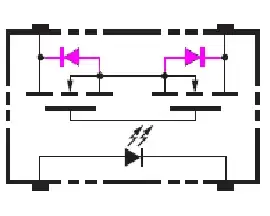
The picture below is from the datasheet of G3VM (another SSR). It also shows body diodes. [Highlighted by me.]
Due to body diode, the N-ch MOSFET can "open the switch" only when body diode is reverse biased. Drain has to be at a higher potential than the source. Otherwise, the diode will conduct, and MOSFET becomes a switch, which doesn't open.
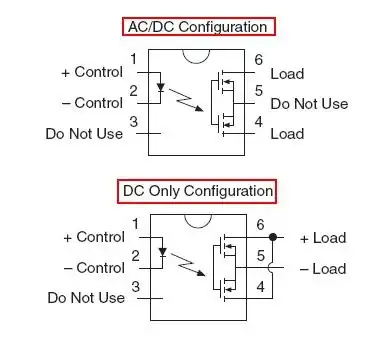
But what to do with the AC? During one part of the AC waveform, the body diode will be forward biased, during another part of the waveform, it will be reverse-biased. This is why the second MOSFET is used. The MOSFETs are connected in series such that their diodes are anti-parallel. They block each-other, and the MOSFETs can "open the switch" at all times. This capability to handle the AC comes at a cost, though. The two MOSFETs are in series and the losses are double.
The LCA717 datasheet doesn't show body diodes. But the body diodes are there nonetheless.
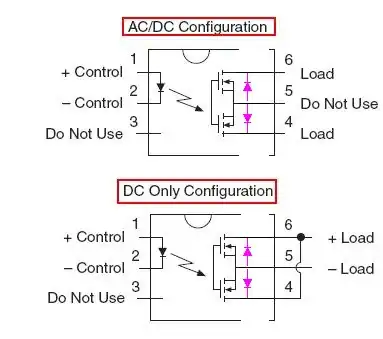
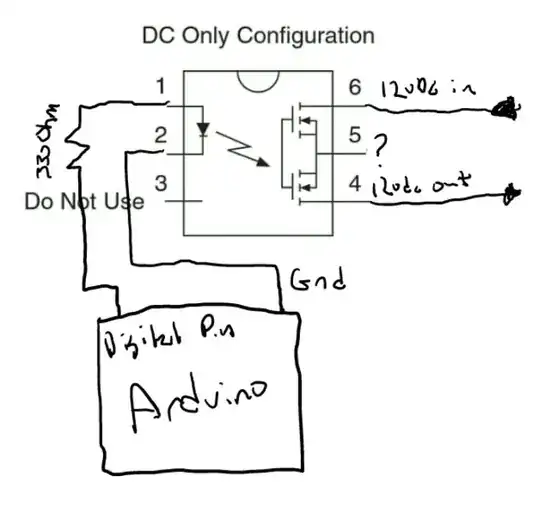
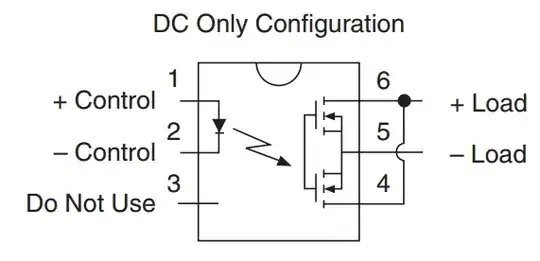
The designers of LCA717 decided to connect the MOSFET sources to the pin. It makes this SSR more versatile. It allows to connect the MOSFETS both: in series (AC/DC configuration), or in parallel (DC-only configuration). Notice that in DC-only configuration, the body diodes are in parallel too, and both of them can become forward biased. Notice that DC mode can handle twice the current.

On the other hand, the designers of the G3VM decided not to connect the MOSFET sources to the pin. Perhaps, they have done that to have fewer pins, in order to keep the device more compact and to keep the cost lower.