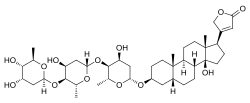
Digitoxin , a phytosteroid and cardiac glycoside found in digitalis .Phytosteroids , also known as plant steroids , are naturally occurring steroids that are found in plants.[ 1] digoxin , digitoxin , diosgenin, and guggulsterone , as well as phytosterols [ a] β-sitosterol .[ 1]
Industrial use
Steroid pharmaceuticals that are identical or similar to human steroid hormones are very widely used in medicine. However, the four-ring structure of a steroid is quite expensive to replicate using direct synthetic methods.
In 1938–1940, American chemist Russell Earl Marker developed the process known as Marker degradation, which converts diosgenin from Mexican Dioscorea yams into 16-dehydropregnenolone acetate, which has a four-ring structure and can be used to synthesize commonly used steroid hormones. Marker's process reduced the price of progesterone from $80/gram in early 1944 to $2/gram in 1951.[ 2]
Also in 1940, American chemist Percy Lavon Julian discovered a process to convert a much more abundant phytosteroid -- stigmasterol from soybean -- into progesterone. Stigmasterol is a byproduct of soybean oil refinement.[ 3] [ 4] [ 5]
References
^ The relationship between phytosteroids and phytosterols is akin to the relationship between steroids and sterols: the latter is a subset of the former, specifically those with a hydroxyl group at the 3-position.
Types of phytochemicals
Terpenoids
Types of terpenes and terpenoids (# of isoprene units)
Basic forms:
Acyclic (linear, cis and trans forms)
Monocyclic (single ring)
Bicyclic (2 rings)
Iridoids (cyclopentane ring)
Iridoid glycosides (iridoids bound to a sugar)
Steroids (4 rings) Hemiterpenoids (1) Monoterpenes 10 H16 )(2)
Acyclic Monocyclic Bicyclic
Pinene (α and β)
Camphene
Thujene
Sabinene
Carene
Monoterpenoids
Acyclic
Citronellal
Citral
Citronellol
Geraniol
Geranyl pyrophosphate
Halomon
Linalool Monocyclic
Achilleol A
Grapefruit mercaptan
Menthol p-Cymene
Thujaplicins (Hinokitiol)
Thymol Perillyl alcohol
Carvacrol Bicyclic
Camphor
Borneol
Bornyl acetate
Eucalyptol Ascaridole
Umbellulone
Sesquiterpenoids (3)
Artemisinin Bisabolol
Cadinene
Cadinol
Cedrene
Chanootin
Farnesyl pyrophosphate
Juniperol
Longifolene
Muurolene
Nootkatin Diterpenoids (4)
Acyclic
Phytol
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
Geranyl-linalool Monocyclic Bicyclic Tricyclic
Cembrene
Forskolin
Manoyl oxide
Pimaral
Pimarol Tetracyclic Resin acids
Abietic acid
Communic acid
Dehydroabietic acid
Isopimaric acid
Lambertianic acid
Levopimaric acid
Mercusic acid
Neoabietic acid
Pimaric acid
Sandaracopimaric acid
Secodehydroabietic acid
Palustric acid
Sesterterpenoids (5) Triterpenoids (6)
Steroids Other
Betulin
Euphol
Lanosterol
Madecassoside
Saponins
Serratenediol
Squalane
Acids
Oleanolic acid
Ursolic acid
Betulinic acid
Moronic acid Madecassic acid
Zizyberenalic acid
Sesquarterpenes/oids (7)
Ferrugicadiol
Tetraprenylcurcumene TetraterpenoidsCarotenoids ) (8)
Carotenes
Alpha-Carotene
Beta-Carotene Gamma-Carotene
Delta-Carotene
Lycopene
Neurosporene
Phytofluene
Phytoene Xanthophylls:
Canthaxanthin Cryptoxanthin
Zeaxanthin
Astaxanthin
Lutein
Rubixanthin
Polyterpenoids (many) Norisoprenoids (modified)
3-oxo-α-ionol
7,8-dihydroionone Synthesis
Terpene synthase enzymes (many), having in common a terpene synthase N terminal domain (protein domain) Activated isoprene forms
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP)
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP)
Phenolic compounds
Types of phenolic compounds
Natural monophenols
Benzenediols
Benzenetriols
Apiole Carnosol
Carvacrol
Dillapiole Polyphenols
Types of polyphenols
Flavonoids
Types of flavonoids
Flavonoids
Anthoxanthins
Flavones Flavonols Isoflavones Neoflavonoids
Flavans
Flavan Flavan-3-ols
Catechin, Gallocatechol, et.c. Flavan-4-ols
Apiforol, Luteoforol, et.c. Flavan-3,4-diols
Leucocyanidin, Leucodelphinidin, et.c. Flavanones Flavanonols
Taxifolin
Aromadendrin, et.c.
Anthocyanidins
3-deoxyanthocyanidins
Cyanidin, Delphinidin, et.c. 3-hydroxyanthocyanidin
Apigeninidin, Guibourtinidin, et.c.
Aurones Chalcones
Miscellaneous
List of phytochemicals in food
C-methylated flavonoids
O-methylated flavonoids
Furanoflavonoids
Pyranoflavonoids
Prenylflavonoids
Methylenedioxy
Castavinols
Flavonoid biosynthesis
Flavonolignans Lignans2 )
Matairesinol
Secoisolariciresinol
Pinoresinol Stilbenoids Curcuminoids Curcumin
Tannins
Types of natural tannins
Hydrolysable tannins
Ellagitannins
Punicalagins
Castalagins
Vescalagins
Castalins
Casuarictins
Grandinins
Punicalins
Roburin A
Tellimagrandin IIs
Terflavin B Gallotannins
Digalloyl glucose
1,3,6-Trigalloyl glucose
Condensed tannins
Proanthocyanidins Polyflavonoid tannins
Catechol-type tannins
Pyrocatecollic type tannins
Flavolans Phlorotannins
Eckol
8,8′-Bieckol
6,6'-Bieckol
Dieckol
Eckstolonol
Diphlorethol
Difucol
Phlorofucofuroeckol A
Tetrafucol A
Trifucol
Bifuhalol
7-Phloroeckol
Phlorofucofuroeckol B Flavono-ellagitannins
Epicutissimin A
Acutissimin A Other Miscellaneous
Tannin sources
Pseudo tannins
Synthetic tannins
Tannin uses
Enological
Drilling
Ink
Tanning
Others
Diarylheptanoids (C6-C7-C6)
Anthraquinones
Chalconoids (C6-C3-C6)
Kavalactones Naphthoquinones (C6-C4)
Phenylpropanoids (C6-C3)
Xanthonoids (C6-C1-C6)
Coumarins and isocoumarins Misc :Polyphenols
Aromatic acids
Aromatic acids
Phenolic acids
Monohydroxybenzoic acids
Aglycones Glycosides
p-Hydroxybenzoic acid glucoside
Dihydroxybenzoic acids
2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (Hypogallic acid)
2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
Ethyl protocatechuate
Gentisic acid
Homogentisic acid
Orsellinic acid
Protocatechuic acid Trihydroxybenzoic acids
Bergenin
Chebulic acid
Ethyl gallate
Eudesmic acid
Gallic acid
Tannic acid
Norbergenin
Phloroglucinol carboxylic acid
Syringic acid
Theogallin Other phenolic acids
Hydroxycinnamic acids
α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid
Caffeic acid
Chicoric acid
Cinnamic acid
Chlorogenic acid
Diferulic acids
Coumaric acid
Coumarin
Ferulic acid
Sinapinic acid Aromatic amino acids
Phenylethanoids Others Misc :
Phenolic compounds
Phlorotannins)
Glucosinolates
Precursor to isothiocyanates
Sinigrin
Gluconasturtiin
Glucoraphanin
Aglycone derivatives
Organosulfides
Indoles
Indole-3-carbinol
3,3'-Diindolylmethane
Allicin
Alliin
Allyl isothiocyanate
Piperine Syn-propanethial-S-oxide Betalains
Betacyanins
Betaxanthins
Indicaxanthin
Vulgaxanthin Chlorophylls Organic acids Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Beta-glucan
Fructan
Lignin
Pectin Misc :List of phytochemicals and foods in which they are prominent
Authority control databases: National